Nonbank Mortgage Servicer Prudential Standards
The Nonbank Mortgage Servicer Prudential Standards establish requirements for capital, liquidity, and corporate governance (including audit, risk management, and board oversight), for nonbank mortgage servicers. The financial condition provisions align with the Federal Housing Finance Agency's Minimum Financial Eligibility Requirements for Seller/Servicers, providing state supervision and enforcement of these common requirements. Though state adoption of the standards is in its early stages, nonbank mortgage servicers licensed in at least one adopting state collectively service 99% of the nonbank mortgage market by loan count.
Prudential Standards for Nonbank Mortgage Servicers
Adoption Status (Updated 1/31/2026)
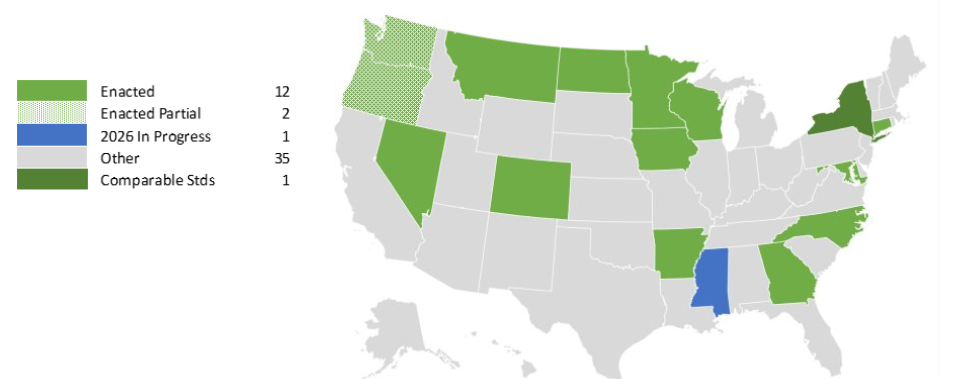
Current Prudential Standards Enactments
About the standards
As nonbank servicers became responsible for a larger share of consumer mortgages, state regulators grew concerned about the absence of a common set of state standards addressing servicers’ capital and liquidity requirements. State examinations of nonbank servicers also identified inadequate corporate governance and board oversight.
These concerns led state regulators to pursue – and subsequently approve – new standards that will require nonbank mortgage servicers to maintain the financial capacity, governance, and risk management practices to adequately serve consumers and investors and simultaneously enhance market stability.
The requirements contained in the standards are only effective through state implementation. State agencies may use the standards to formulate law, rule, guidance, or procedure under their individual jurisdictional authority or legislative process. The standards specify the importance of consistent adoption to regulate multistate entities and to minimize regulatory burden. To that end, CSBS is working with states to achieve consistent nationwide implementation.
Key highlights of the standards include:
- The standards focus on two main areas: financial condition, i.e., capital and liquidity, and corporate governance, i.e., board of directors, internal and external audits.
- The standards align with existing federal minimum eligibility requirements, wherever practical, to minimize regulatory burden for servicers.
- The standards apply to servicers that service at least 2,000 loans and operate in two or more states and cover both agency and non-agency servicing.
- The standards do not apply to:
- small servicers that meet a de minimis cutoff
- not-for-profit mortgage servicers
- housing agencies
- The standards provide state regulators with flexibility to increase requirements for high-risk servicers or even suspend the requirements in times of economic, societal, or environmental volatility.
Documents
- Model Language for Standards
- State Prudential Standards and Regulations
- Arkansas Prudential Standards Statute
- Colorado Prudential Standards Statute
- Connecticut Prudential Standards Statute
- Georgia Prudential Standards Statute
- Iowa Prudential Standards Statute
- Maryland Prudential Standards Regulation
- Minnesota Prudential Standards Statute
- Montana Prudential Standards Statute
- North Carolina Prudential Standards Statute
- North Dakota Prudential Standards Statute
- Nevada Prudential Standards Statute
- Wisconsin Prudential Standards Guidance
Get Updates
Subscribe to CSBS
Stay up to date with the CSBS newsletter

